Fish Identification
Bass Identification Chart
* Largemouth bass X Alabama bass and smallmouth bass X Alabama bass hybrids may have a small patch of teeth on the tongue.
Additional information on these and other species can be found at ncwildlife.org/fishing
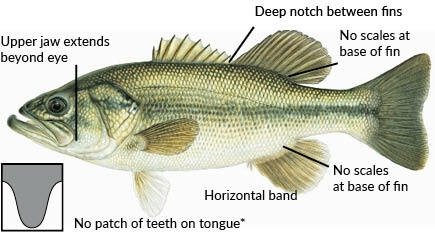
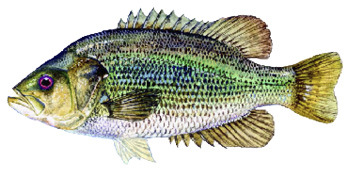
Largemouth Bass
Found statewide
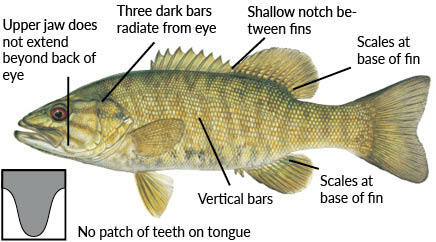
Smallmouth Bass
Found west of I-77 & in the Uwharrie and Dan rivers
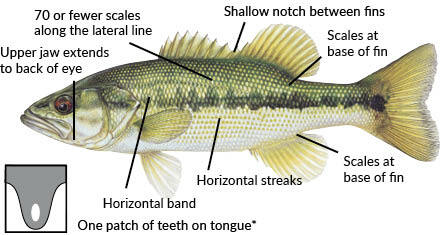
Spotted Bass
Found west of I-77 & Cape Fear River
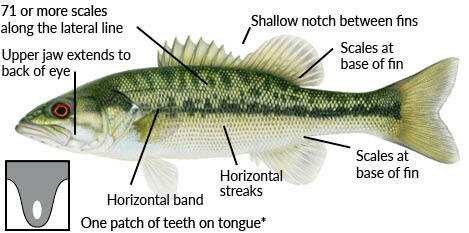
Alabama Bass (Invasive)
Found statewide
Morone Identification Chart
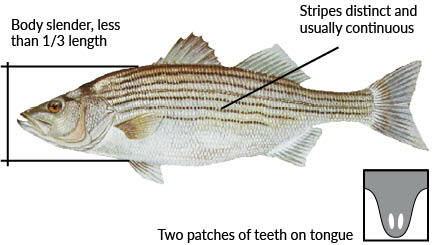
Striped Bass
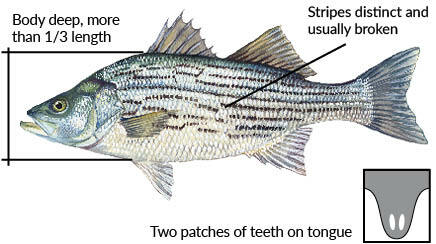
Bodie Bass (striped bass hybrid)
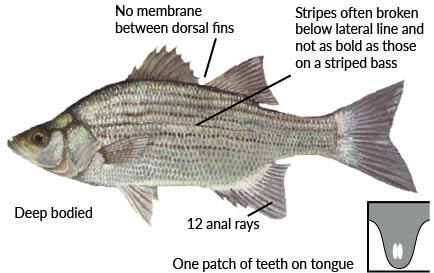
White Bass
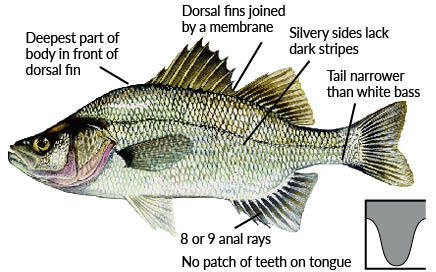
White Perch
Species Identification Chart
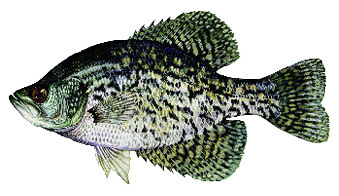
White Crappie
- 5–6 dorsal spines
- 5–10 dark vertical bars on each side
- Best populations found in Piedmont reservoirs and rivers

Black Crappie
- 7–8 dorsal spines
- Many dark spots on sides and fins
- Common in large rivers in Coastal Plain, clear ponds, natural lakes and reservoirs
Bluegill
- Ear flap entirely black
- Pattern of vertical bars on sides
- Most common sunfish in state

Pumpkinseed
- 4–8 wavy lines, often bright blue, on cheek
- Ear flap black with orange-red spot

Redbreast Sunfish
- Bluish streaks on cheeks and around eyes
- Long, narrow ear flap entirely black

Redear Sunfish
- Commonly called shellcracker
- Red or orange edge along ear flap
- No blue lines along cheeks

Roanoke Bass
- Similar shape as rock bass, but is dark olive-green to olive brown
- No scales on cheek
- Only found in Dan, Deep, Neuse, Tar, & Uwharrie rivers
Rock Bass
- Olive-green top and gold or brassy-colored sides
- Scales on sides have dark spots, forming striped-like appearance
- Unlike Roanoke bass, have scales on cheeks and dark spot near ear flap

Warmouth
- Similar in appearance to rock bass, but has large mouth, similar to bass
- Anal fin has three spines compared to six of rock bass
- Three or four stripes radiate from eyes across to cheek and gill cover

Brown Trout
- Golden brown to olive with yellowish sides
- Dark spots circled with light yellow or white on back and sides
- Some fish also have orange or red spots on sides
- Reclusive fish, often hanging out near fallen trees and undercut banks

Rainbow Trout
- Broad lateral stripe, pinkish to red, on sides
- Heavy black speckling on entire body
- Prefer faster currents, such as riffles and swift runs

Brook Trout
- Sometimes called speckled trout
- Greenish brown with light red spots on sides
- Dark, worm-like lines on back
- White edges on fins, including tail
- Only native trout

Yellow Perch
- Greenish-yellow along back with dark bands on sides
- Two separate dorsal fins
- Very sharp edge on gill covering

Walleye
- Largest member of perch family
- Found in streams and rivers, but prefer lake environments
- Normally found in depths of 20–60 feet

Muskellunge
- Member of pike family
- Sides usually have vertical bars or blotches and fins have spots or streaks
- Has 12–18 small pores underneath the jaw
- Prefers cool rivers and lakes with plentiful woody debris, vegetation and rocky habitat

Chain Pickerel
- Close relative of muskellunge
- Named for chain-like pattern on sides
- Black bar beneath eyes distinguishes it from small muskellunge

Blue Catfish (Invasive east of Continental Divide)
- Anal fin has straight outer edge and 30–36 rays
- Common in large rivers and often favor faster currents than other catfish
- Because of competition with other species (striped bass) for prey, should not be moved from one waterbody to another

Bullhead Catfish
- Five species of bullhead exist in North Carolina—brown (pictured), yellow, black, flat and snail

Channel Catfish
- Deeply forked tail with black spots on back and sides
- Anal fin is round with 24–29 rays
- Highly adaptable, living in ponds, streams, rivers, lakes and reservoirs

Flathead Catfish (Invasive east of Continental Divide)
- Broad, flat head with lower jaw protruding beyond upper jaw
- Should not be moved from one waterbody to another
- Feeds primarily on live fish and has been associated with declines of several native fish species

White Catfish
- Blue-gray above, fading to gray on sides with white belly
- Distinguished from channel catfish by much wider head and lack of black spots on sides
- Aggressive feeders and feed more during daylight than other catfish


